What is Account-Based Selling (ABS)?
Account-based selling (ABS) is a targeted B2B sales strategy where specific companies, referred to as “accounts,” are the primary focus. Often, these accounts already have some pre-existing relationship with your business. ABS emphasizes understanding and catering to the client’s current needs and introducing relevant products or services to them. This approach can focus on the department where the relationship exists or expand to other departments.
A common term associated with ABS is “land and expand,” where sales professionals begin with a smaller transaction to build trust and then aim to grow revenue from the account over time. Effective ABS strategies often involve detailed relationship mapping to identify and nurture key stakeholders within target accounts.
10 tips for a successful Account Based Selling strategy
When implementing ABS, it’s crucial to approach it systematically. Here are 10 actionable tips to boost your ABS strategy:
1. Know when to use ABS
Not every sales scenario suits ABS. It’s most effective for selling to large organizations with multiple decision-makers and complex buying processes. Avoid using ABS for small, transactional sales where a broader approach may yield better results.
2. Collaborate with marketing
ABS often works best alongside account-based marketing (ABM). Ensure your sales and marketing teams align on goals, share insights, and collaborate to create personalized and persuasive content tailored to each stage of the buyer’s journey. Open communication and shared reporting are key.
3. Identify suitable target accounts
Leverage your CRM to analyze which industries or accounts have previously shown the most success. Collaborate with senior colleagues to define an ideal customer profile (ICP) that pinpoints the types of accounts most likely to benefit from your solutions.
4. Map out relationships
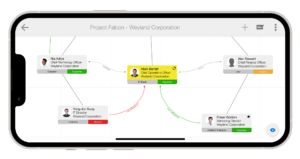
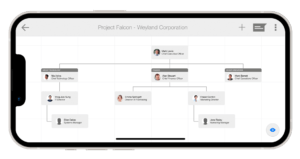
Understanding the decision-making process within your target accounts is vital. Large organizations often have multiple influencers and decision-makers. Build a strong relationship with at least one champion in the organization, and if possible, establish multiple connections to strengthen your position. Utilize tools like ContactBase to create detailed maps of connections and hierarchies within an organization, helping you navigate complex structures.
5. Leverage technology
Beyond your CRM, utilize advanced tools like sales AI platforms (e.g., 6sense) to gain insights, predict buying behavior, and optimize your sales strategies. These technologies can help you make data-driven decisions and build stronger client relationships.
6. Do thorough research
Study your target accounts by reviewing any available reports, press releases, or strategic documents. This research can help you anticipate their needs, understand their pain points, and identify competitors they may be considering. Comprehensive knowledge positions you as a trusted advisor.
7. Maintain real-time data updates
Consistency in data is crucial for ABS. Ensure your team’s systems are always updated in real-time to prevent miscommunication or errors. Accurate data fosters trust and streamlines the sales process.
8. Monitor activity across teams
Track all client interactions, from marketing emails to sales calls. Ensure your messages are consistent and relevant. Coordination is particularly important if you’re part of a larger organization with multiple departments targeting the same account.
9. Adopt a sales-only focus
Focus on demonstrating your expertise in the client’s industry. Stay informed about market trends, emerging technologies, and your competitors. Build a reputation as an industry authority to keep your clients engaged and loyal.
10. Analyze and optimize sales effectiveness
Regularly review your sales performance data to identify trends and areas for improvement. By learning from past successes and failures, you can refine your approach and avoid repeating mistakes.
Why choose Account-Based-Selling?
While ABS isn’t suitable for every business model, it offers significant benefits for companies targeting large, complex organizations. Here’s why ABS might be the right fit for your sales strategy:
1. Accurate sales forecasting
ABS provides greater visibility into your sales pipeline, enabling you to make more precise predictions about future opportunities.
2. Controlled sales processes
ABS allows you to determine the right accounts to target, the timing of your outreach, and the most relevant solutions to offer. This level of control ensures a tailored approach for each account.
3. Focus on high-value clients
Instead of spreading efforts thin, ABS helps you concentrate on the 20% of clients most likely to drive 80% of your revenue. This focus maximizes impact and efficiency.
4. Risk mitigation
With ABS, you build relationships with multiple stakeholders within an organization. This reduces the risk of losing the account if a key contact leaves or is unavailable.
Conclusion
Account-based selling is a powerful strategy for businesses targeting large, complex accounts. By following these 10 tips, collaborating across teams, and leveraging the right tools—including relationship mapping—you can strengthen relationships, grow revenue, and achieve long-term success. Whether you’re just starting with ABS or refining your approach, these strategies will help you stand out in competitive markets.